I finally made the jump from primarily console to PC gaming shortly after building my own in 2020, which was the absolute worst time to start a new hobby due to the then-soaring costs of PC components.
Since I built my first PC, I’ve spent a lot of time upgrading it, adding new parts, and making it a lean, mean machine. However, if there’s one thing that always bothered me after installing a secondary NVMe for gaming, it’s the slow installation process of Steam or any other library.
After venting about the issue on a Discord call with a few friends, one of them mentioned something that hadn’t even crossed my mind. It had nothing to do with Steam download locations or anything of the sort, but a simple trick made my downloads go from zero to hero in no time: write caching.
So, what does write caching do, exactly?
Turning this off could unlock the potential of your SSD or NVMe
Before turning off write caching, I wanted to learn more about the process. Simply put, write caching utilizes your PC’s RAM to cache data being written onto your disk. Using an SSD or NVMe drive can significantly slow your data write speeds.
Since write caching uses your RAM to store write commands, it can cause conflicts when used with an SSD or NVMe that has a high write speed. I didn’t realize it at the time, but roughly two years of slow Steam downloads were significantly boosted by turning off this setting.

- Capacity
-
1,024GB
- Speed
-
Up to 3,200 MB/s
- Connection
-
M.2 Connection
- Brand
-
Western Digital
Will disabling write caching damage your drive?
Storage isn’t cheap, so taking care of it is a great idea
One of the biggest things I worried about before trying this for myself was the possibility of damaging my drive or losing data if I forgot to re-enable write caching after I was done with my Steam downloads. As of the time of this writing, I have seen no negative impact on my daily activities, from work to play. It’s been roughly a month since I tried doing this myself, and I’ve personally seen no impact during my daily activities on my PC.
On the contrary, enabling write caching has a higher risk of losing data or corrupting data, especially if a user were to power down their computer or lose power before a write is done. However, as with any sort of tampering with OS-level settings, I always like to express a bit of additional caution when playing with settings like this.
If you feel more comfortable turning write caching back on after you’ve finished a Steam download, that’s completely valid and a genuinely good idea. It’s a few extra steps, for sure, but for that improved download speed, it’s worth a few extra clicks.
Disabling write caching solved my issue quickly
This setting is on by default, and can affect all SSDs differently
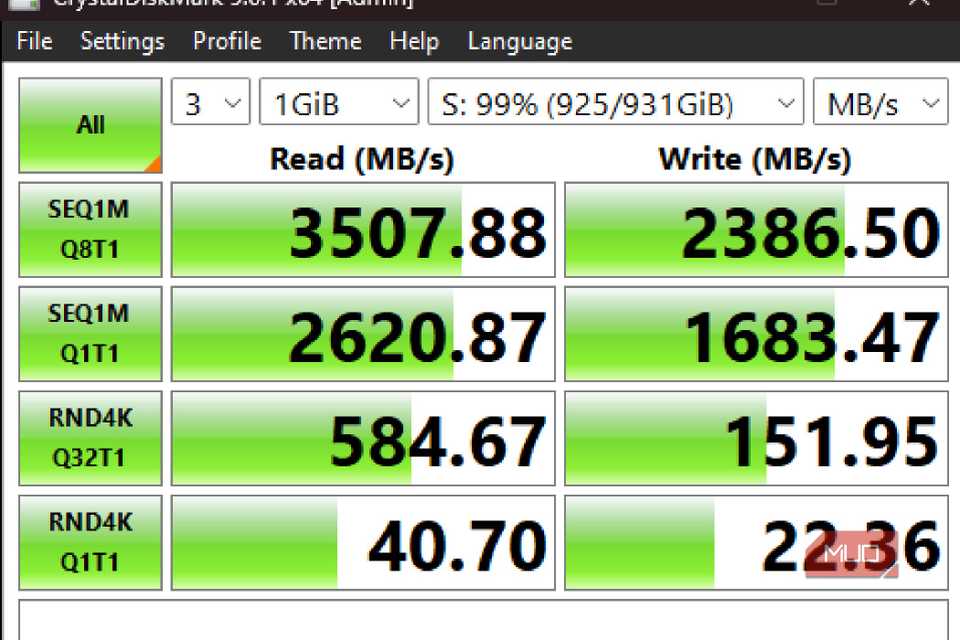
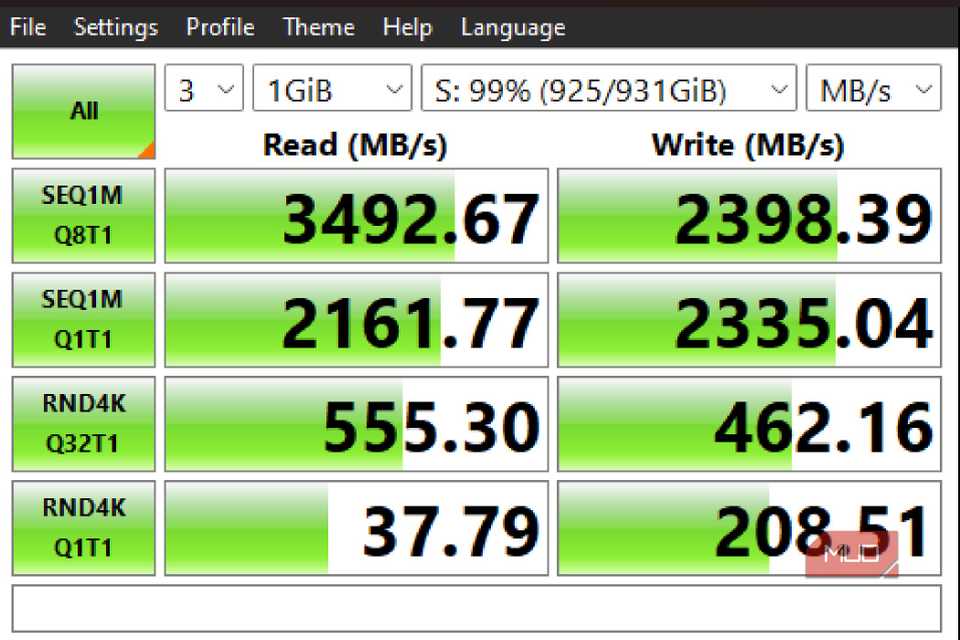
I wanted to do a before-and-after test to see how much of a difference turning off write caching could make. Running CrystalDiskMark, a freemium program that allows users to test their read/write speeds on any disk in their system, I was shocked to see that, on paper, there wasn’t much difference.
Running the initial test with write caching turned on, I saw a read speed of 3492.67MB/s and a write speed of 2398.39MB/s. Once I had turned this setting off, I had read speed of 3507.88MB/s and a write speed of 2386.50MB/s, and I could only think of how that could be correct. How could it be writing slower, but installing Steam games slower with write caching turned on?
That’s because write caching was installing the games in chunks, rather than in whole parts, slowing down the download and installation process rather dramatically on my NVMe drive. Sometimes, testing along these lines may look counterintuitive, but seeing the results firsthand, I can confirm that turning off write caching can speed up write speeds on specific downloads.
How to disable write caching in Windows 11
Make sure you select the correct disk for this portion
For a setting like this, you may imagine that it would be hiding in the depths of the Windows operating system. In reality, it’s hiding just under the surface and only a few clicks away from being turned off. If you’re ready for some buffs on your PC, follow these simple steps to turn off this setting.
-
To disable write caching, use the Windows search bar to search for Device Manager.
-
Inside this window, select the option for Disk Drives.
-
Right-click on the drive that you’d like to disable write caching on, and select Properties.
-
In the new window, select Policies, and deselect write caching on the device.
- Click on OK to finish the process, and test your download speed on Steam, Xbox PC Game Pass, or any other library to see the difference.
Unless you feel the need to turn write caching back on, there are really no downsides to just leaving this setting off.
Was it worth turning off write caching?
To me, the download boosts speak for themselves
I’ve been gaming for as long as I can remember, even back in the DOS days. Since then, the size of games and other files continues to balloon, and while my internet speed continues to increase, I’d like my downloads to keep up with it. I’ve realized now that turning off write caching was one of the best decisions I’ve made in a long time.
While the benchmarks may not show a tremendous difference, my NVMe and downloads folder can speak for themselves. My download speeds have increased, my write speeds have increased, and the number of games I can download before powering off my PC has never been higher. So far, roughly a month in, I’ve seen no downsides to this, and I suggest giving it a try if you’ve been struggling with your library of Steam titles.




