Tired of repeating the same routine tasks on your PC? With Task Scheduler, you can automate everything from daily cleanups to launching your favorite apps at startup. It’s built into Windows and easier to use than you might think.
What Is Task Scheduler?
Task Scheduler is a built-in Windows utility that lets you schedule and automate tasks to run at specific times or under certain conditions. Whether it’s launching an app when you log in or running maintenance scripts every weekend, Task Scheduler does the work in the background—no clicks required.
It’s especially useful for routine jobs like cleaning temporary files or ensuring your antivirus scan runs weekly. Once configured, it just works. Think of it as your own personal assistant for system maintenance.
How to Access and Navigate Task Scheduler
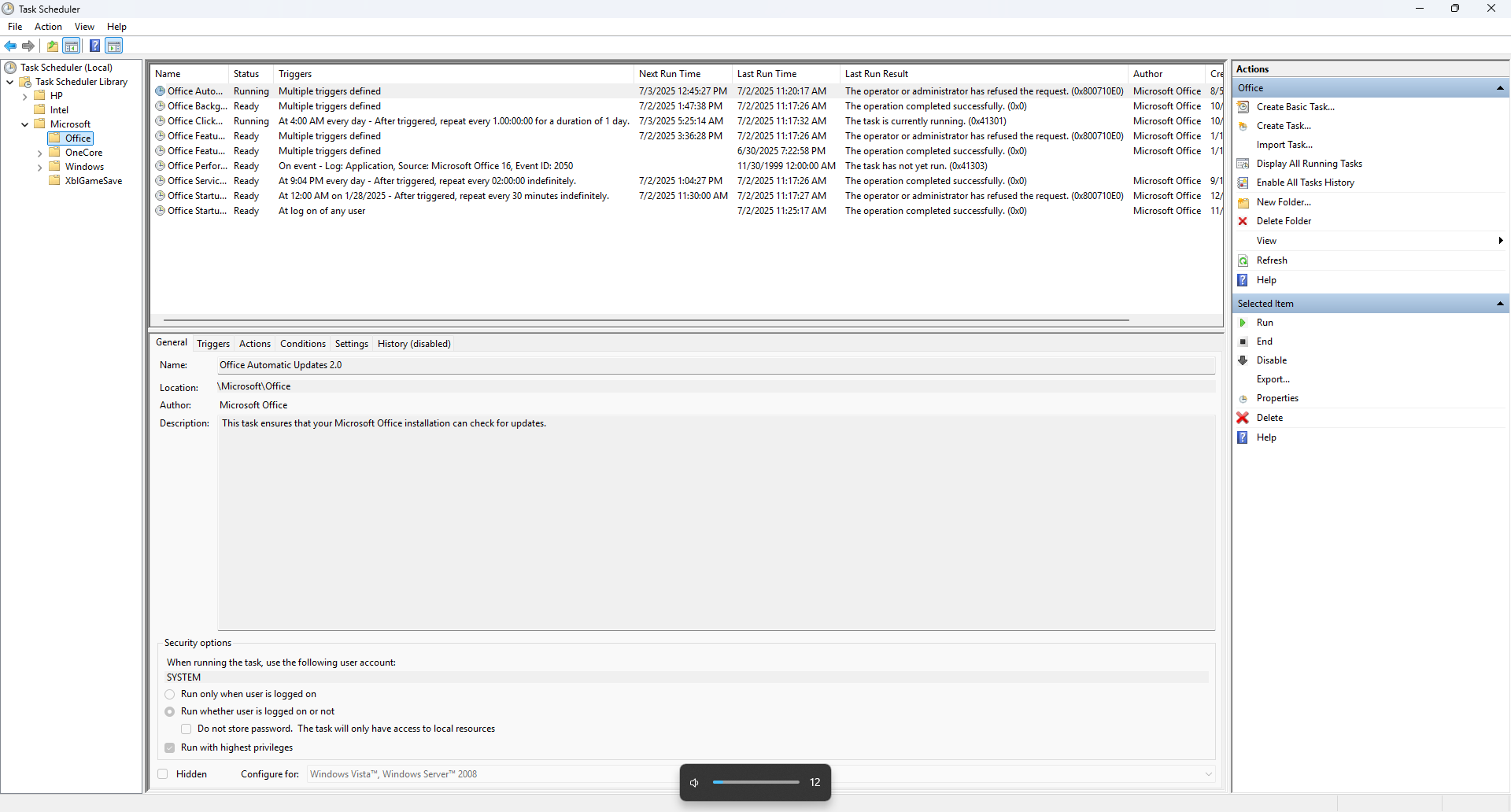
To get started, open Task Scheduler from the Start menu, Control Panel, or by typing taskschd.msc in the Run dialog. The interface might look a bit dated, but it’s straightforward once you know what to look for.
On the left, you’ll see the Task Scheduler Library, where all tasks are stored. The middle pane shows task details, and the right-hand Action Pane lets you create or manage tasks. When editing a task, you’ll see tabs for General settings, Triggers, Actions, Conditions, and Settings. Each tab gives you control over when and how your task behaves.
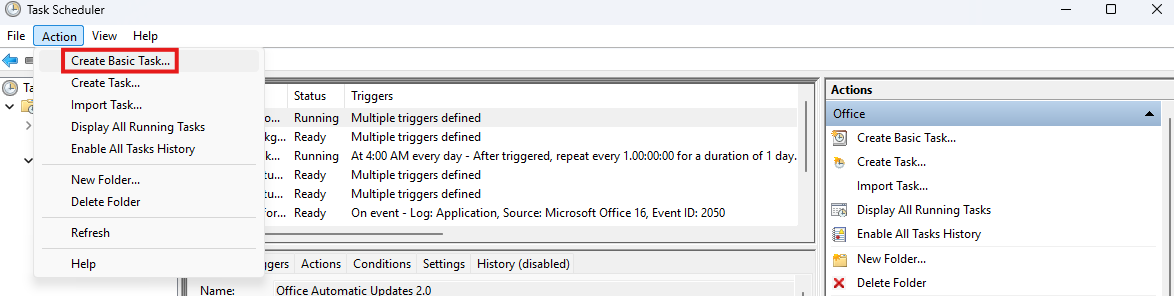
Creating Your First Basic Task
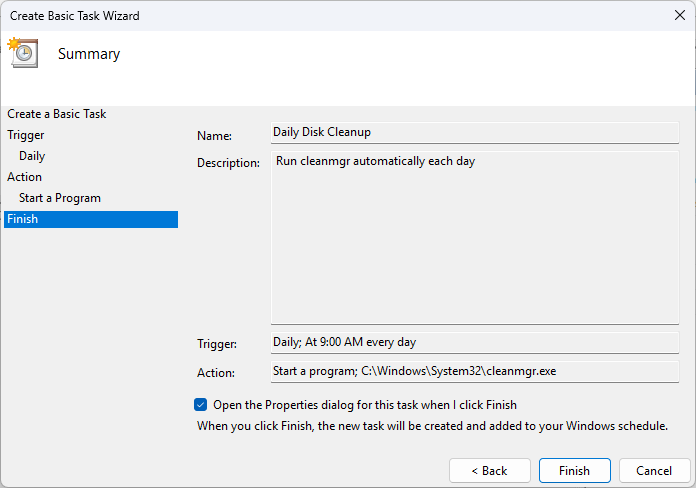
The easiest way to jump in is by using the Create Basic Task wizard. It guides you step-by-step through setting up something simple, like opening Notepad every day at 8 a.m.
You’ll start by naming the task and writing a short description. Next, choose a trigger—this is the event that starts the task, such as a time of day or user logon. Then you pick an action, like starting a program or sending an email. After reviewing the summary, hit Finish, and your task is ready to go.
Automating Maintenance Tasks
Task Scheduler shines when it comes to system maintenance. You can set up disk cleanup to run automatically using the built-in cleanmgr tool. Or, if you have a batch file that clears temporary files or logs, you can schedule it to run weekly or monthly.
Want to keep your antivirus up to date? You can schedule full scans at night or during idle hours. Just be sure to enable the option to “Run with highest privileges” if the task requires administrative access. You can also use Conditions to avoid running the task while you’re actively using the computer.
Automating Software Launches
If you like your work apps ready the moment you log in, Task Scheduler can make that happen. Just set a task to trigger “At log on” or “At startup,” and point it to the executable file of the app you want to launch.
This is more flexible than the traditional Startup folder, especially if you want tasks to run only under specific conditions or with elevated permissions. It’s perfect for productivity tools, cloud sync apps, or anything you want running as soon as the system boots.
Advanced Features and Options
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, the “Create Task” option gives you much more control. You can set multiple triggers, such as running the same task both at startup and on a weekly schedule.
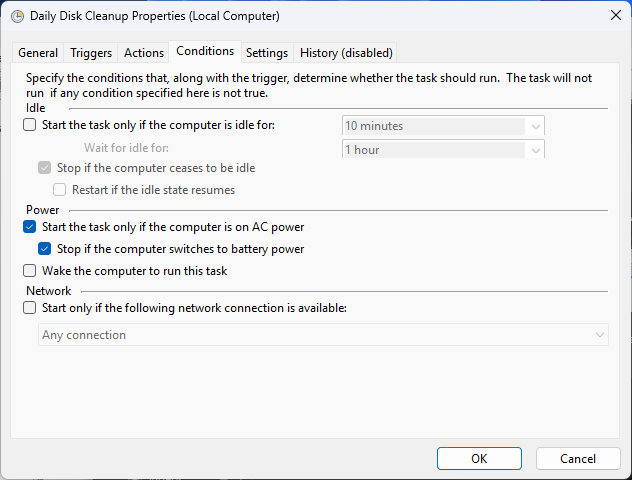
Conditions let you fine-tune behavior—only run if the computer is idle, on AC power, or connected to a certain network. Under Settings, you can configure what to do if the task runs longer than expected or fails to start.
The Task History tab helps you troubleshoot. If something doesn’t run as expected, this is the first place to check.
Tips and Troubleshooting
If your task isn’t running, start by checking the Task History to see if there was an error. Make sure the path to your program or script is correct, and check that the task is enabled.
Some tasks need administrative privileges, so be sure to select “Run with highest privileges” under the General tab. You can also manually run a task from the Action Pane to test it right away.

Related
Enable the (Hidden) Administrator Account on Windows 7, 8, 10, or 11
Many people familiar with prior versions of Windows are curious what happened to the built-in Administrator account that was always created by default. Does this account still exist, and how can you access it?
Permissions, typos, or misconfigured triggers are often the cause of problems. A few tweaks will usually solve the issue.
While Task Scheduler handles most automation needs, there are times when you might want something more advanced. PowerShell scripts can automate more complex workflows. Third-party tools like AutoHotKey offer even deeper control, including keyboard automation and window management.
Still, for anything time-based or trigger-based, Task Scheduler remains one of the most stable and lightweight options available.
Task Scheduler may not look flashy, but it’s a powerful tool for anyone looking to save time and reduce repetitive work. Whether you’re launching apps, running scripts, or keeping your system tidy, it’s worth learning how to make it work for you.
Start with something simple, test it out, and before long you’ll be automating tasks you didn’t even realize could be automated. If you want to dig deeper, Microsoft’s official documentation is a great place to explore more possibilities.