If you’ve ever opened a command-line window on Windows and wondered which tool you should be using, you’re not alone. Between Command Prompt, PowerShell, and Windows Terminal, knowing when to choose each can make a big difference in how efficiently you work.
Understanding the Basics
Command-line tools have been essential to Windows for decades. They help users perform tasks quickly and manage systems more effectively. However, not all command-line tools are created equal. Knowing the differences between Command Prompt, PowerShell, and Windows Terminal can help you pick the right one for the job and avoid unnecessary headaches.
Let’s start with a look at the basic characteristics of each of these tools.
Command Prompt
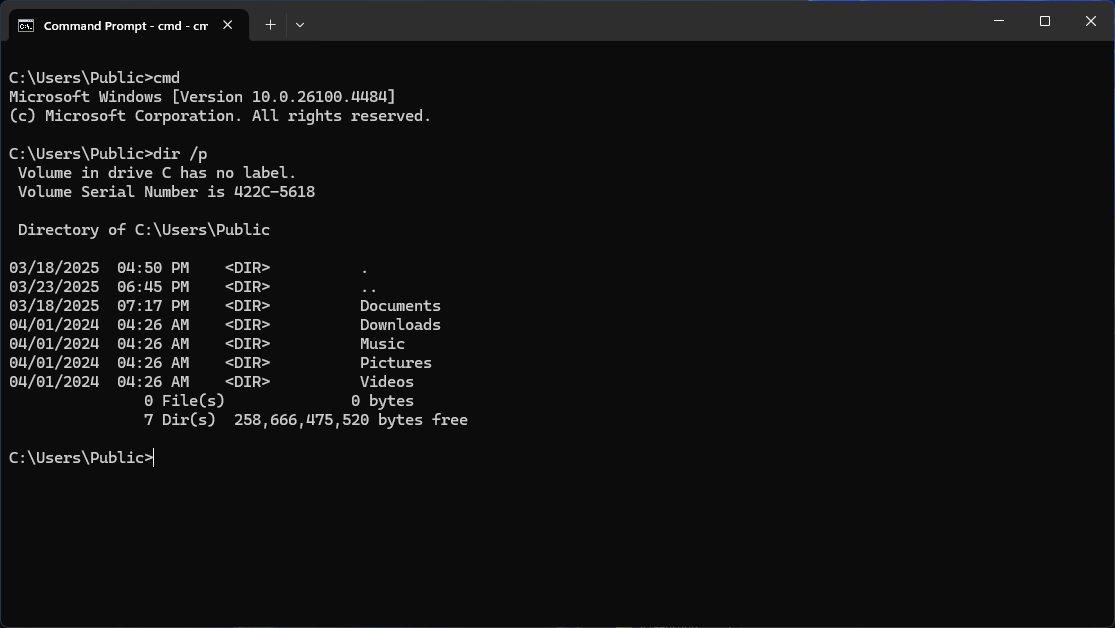
Command Prompt, often called CMD, is a familiar tool for many users. It traces its roots back to the MS-DOS days and provides a simple, text-based interface for executing commands. While it’s not designed for complex operations, it’s perfect for quick, straightforward tasks like running simple scripts or managing files.
PowerShell
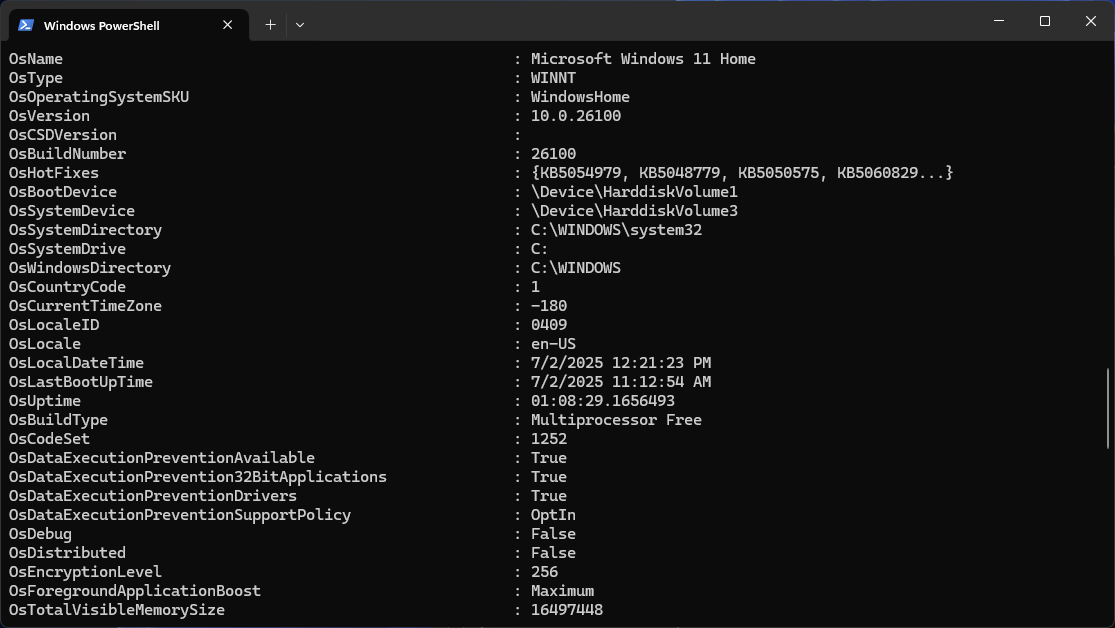
PowerShell steps things up by offering a powerful scripting environment. Unlike CMD, which deals mainly in plain text, PowerShell works with objects, making it more versatile for managing Windows systems. It integrates tightly with .NET and can handle advanced tasks like automating system configurations and accessing the Windows Registry.
Windows Terminal
Windows Terminal is the newest member of the group. Rather than being a shell itself, it serves as a modern interface for hosting multiple shells. You can run CMD, PowerShell, and even Linux distributions through Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) all within a single, customizable window. With features like tabs, Unicode support, and GPU-accelerated rendering, it makes multitasking smoother and more efficient.
Side-by-Side Feature Comparison
Although there is some overlap, each tool also has its own unique features.
Command Prompt
- Text-based shell
- Released in 1987
- Basic scripting support (batch files)
- Minimal customization
- Ideal for quick commands and legacy operations
PowerShell
- Object-based shell and scripting language
- Released in 2006
- Supports full scripting with loops, conditions, and system access
- Moderate customization options
- Best for system administrators and automation experts
Windows Terminal
- Interface for multiple shells
- Released in 2019
- Runs CMD, PowerShell, WSL, and others
- High customization with themes, fonts, and tabs
- Perfect for power users managing diverse environments

Related
7 Ways to Open Windows Terminal on Windows 11
Windows Terminal is as good as the terminal found on Macs or any Linux distro.
Here are some suggestions to help you choose the right tool for the job at hand.
Simple System Tasks
For basic activities like checking your IP configuration, moving around directories, or quickly renaming files, Command Prompt is often the fastest and simplest choice. It launches quickly and handles these tasks with ease.
Complex Scripts and Automation
If you need to automate repetitive tasks, manage system settings, or pull structured data from your system, PowerShell is your best bet. Its scripting capabilities go far beyond what CMD can offer, and its deep integration with Windows makes complex tasks much easier.
Managing Multiple Sessions and Environments
When you find yourself working with multiple shell environments—maybe CMD for one task, PowerShell for another, and WSL for development—Windows Terminal shines. Its tabbed interface lets you switch between tasks without cluttering your desktop with multiple windows.
How Do You Actually Use Them?
Following are some practical examples of how you might use each tool.
Renaming Files in Bulk
If you just need to rename all TXT files to TXT, Command Prompt can handle it quickly. But if you need conditional logic or more complex renaming patterns, PowerShell provides the flexibility you need with its scripting capabilities.
Retrieving System Information
CMD’s systeminfo gives you a quick snapshot of system details. PowerShell, on the other hand, can deliver much deeper insights with commands like Get-ComputerInfo, which returns structured, detailed data that’s easier to filter and manipulate.
Running Simultaneous Sessions
With Command Prompt and PowerShell, you’re generally stuck opening multiple windows. Windows Terminal changes that by letting you run multiple tabs in a single, streamlined window—whether you’re toggling between PowerShell scripts or a Linux shell.

Related
7 Useful Batch Files You Can Create to Automate Tasks on Windows 11
Including launching multiple apps at once.
Compatibility and Integration
Depending on what version of Windows you are running and what you want to do, you’ll find that these command line tools have varying levels of compatibility and system integration.
Command Prompt
Works on virtually every version of Windows, making it a reliable fallback when nothing else is available. It doesn’t require special dependencies and is well-suited to older scripts and tools.
PowerShell
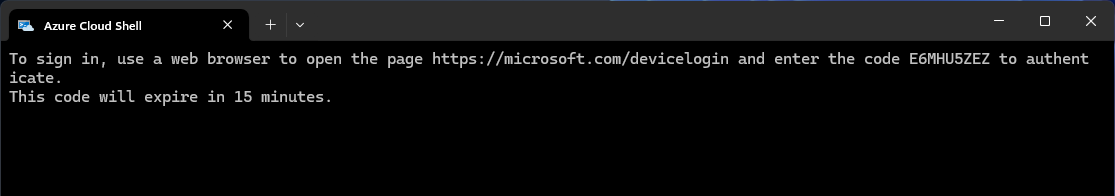
Goes deeper into the Windows ecosystem, offering hooks into services like Azure and Office 365. Plus, with the introduction of PowerShell Core, it’s now available across platforms including macOS and Linux.
Windows Terminal
Acts as a one-stop shop for all your command-line needs. Whether you’re using traditional CMD, scripting in PowerShell, or working in a Linux environment, Windows Terminal can host them all with a highly customizable experience.

Related
5 Terminal Commands You Can Run on Windows that Give Big Hacker Vibes
No harm, no foul—only hacker vibes.
If you’re looking to perform quick and simple tasks, Command Prompt is a great choice. When you need to dive deeper into scripting, automation, or system management, PowerShell has the tools to get the job done efficiently. And if you want the flexibility to work with multiple environments in a visually modern and customizable way, Windows Terminal should be your go-to interface.
Each of these tools has its strengths, and they’re not necessarily in competition with each other. Think of them as different tools in a well-stocked toolbox. Understanding what each does best—and when to use them—can help you work smarter, not harder. Whether you’re managing files, writing powerful scripts, or switching between environments, Windows offers the right tool for the job. It’s just a matter of picking the right one for your needs.